国際査読あり
EarWiggl’In: The Ear Wiggling Input Method for Smart Glasses using Pressure Sensors on Nose Pads
Abstract
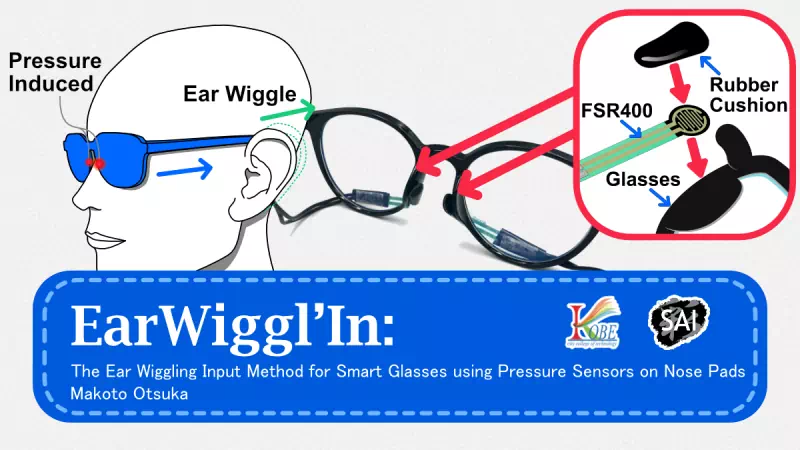
Eye trackers on smart glasses enable cursor control, but an additional input trigger is required for target selection. EarWiggl’In introduces a hands-free and eyes-free input system for smart glasses that utilize pressure sensors on the nose pads. The system detects input by measuring the pressure induced when the glasses are pulled back with the ear wiggling. A user study was conducted to evaluate the input speed of ear wiggling, eight ear wiggle gestures, and the workload using NASA-RTLX. Results indicated that ear wiggling input speed was comparable to, though slightly slower than, pressing a button with a finger, with an average delay of 36.28[ms]. Additionally, eight gestures were analyzed, revealing different amplitudes, numbers of peaks, and durations depending on the gesture.
Poster
Document
Information
Book Title
CHI EA '25: Proceedings of the Extended Abstracts of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems
Volume
898
Number
Date
Pages
1-7
Citation
Copied!
Makoto Otsuka, EarWiggl’In: The Ear Wiggling Input Method for Smart Glasses using Pressure
Sensors on Nose Pads, CHI EA '25: Proceedings of the Extended Abstracts of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 898巻, 号, 7 pages